Table of Contents
Plant Pot Scale
Goal: Development of Wifi or BLE enabled scale to measure the weight of plant pots for an experiment of Anna-Lea.
Weight Range Estimation
The intended pot size has $d = 20\, \mathrm{cm}$ diameter and a volume of $V = 7.5\, \mathrm{L}$.
The folowing rough estimate yields just design values for the expected dynamic range.
Maximum Mass: Saturated Sand
Assumptions (This worst case does not occur in practice, because the use of sand is not quite likely):
Pot completely filled with sand, density of sand $\rho_s=1.6\, \mathrm{kg/L}$, porosity $\eta = 40\,\%$ (depends strongly on compaction), pore space completely filled with water (density $\rho_w=1\, \mathrm{kg/L}$. The total mass $m$ is the sum of mass $m_s$ of sand and $m_w$ of water:
$m = m_s + m_w = \rho_s \cdot V + \eta \cdot \rho_W \cdot V = (\rho_s + \eta \cdot \rho_W) \cdot V = (1.6 + 0.4\cdot 1)\,\mathrm{kg/L} \cdot 7.5\,\mathrm{L} = 15\,\mathrm{kg}$.
Here the mass of the plastic pot itself is neglected!
Dry sand alone would have a mass of $m_s = \rho_s \cdot V = 12\,\mathrm{kg}$
Maximum mass of water under saturation: $m_w = \eta \cdot \rho_W \cdot V = 3\,\mathrm{kg} $
It follows:
$1\,\%\mathrm{vol} \, \widehat{=} \, 3000/40\,\mathrm{g} = 75\,\mathrm{g}$.
| For Sand | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Saturation $S$ | Volumetic Water Content $\Theta$ | Mass of Water $m_w$ | Total Pot Filling Mass $m$ |
| $0\,\%$ | $0\,\%\mathrm{vol}$ | $0\,\mathrm{g}$ | $12000\,\mathrm{g}$ |
| $100\,\%$ | $40\,\%\mathrm{vol}$ | $3000\,\mathrm{g}$ | $15000\,\mathrm{g}$ |
Minimum Mass: Dry Potting Soil
Density of potting soil: $\rho_p = 0.5\,\mathrm{kg/L}$
Mass of dry potting soil: $m_p = \rho_p \cdot V = 3.75\,\mathrm{kg} = 3750\,\mathrm{g} $
Design Values
Design dynamic range of the pot irrigation experiments: $3000\,\mathrm{g} \le m \le 15000\,\mathrm{g}$
The scale should be designed for $20\,\mathrm{kg}$ max weight (mass).
Futher Specs
Load Cell
Max mass of $20\,\mathrm{kg}$, based on the dedicated HX711 24-bit ADC, e.g. from Joy-IT, e.g. sold by Reichelt
According to the datasheet the accuracy is $0.02\,\%$ of full scale (F.S.), i.e. $0.02\,\% \cdot 20\,\mathrm{kg} = 2\cdot10^{-4} \cdot 20\,\mathrm{kg} = 4\cdot 10^{-3}\,\mathrm{kg} = 4\,\mathrm{g}$.
This corresponds to a volumetric water content (sand example above) of $\Delta \Theta \approx 1/20 \,\%\mathrm{vol}$. This is much more than needed in real experiments.
We would rather assume an experimental measurment error of at least(!) $1\%\mathrm{vol}$. The tree in the pot is growing, too, and changes the total mass measures by the scale!
MC
- Wifi or Bluetooth enabled enabled microcontroller
Powerbank
- Battery driven, i.e. with USB power bank ($5000\,\mathrm{mAh}$)
PP Menu Bowl
Outer size: Breite 178 mm, Länge 227 mm, Höhe 49 mm
Usable inner size: Breite 157 mm, Länge 207 mm, Höhe 48 mm
First Prototype
Hardware:
| hardware | product page |
|---|---|
| ESP32S3 | seedstudio |
| 20kg load cell with hx711 adc | reichelt |
| ds3231 real time clock | makershop |
| 2000 mAh LiPo-battery | eckstein |
Operation
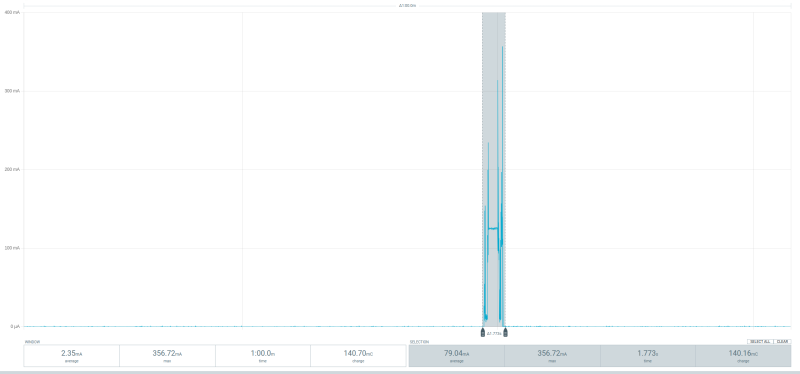
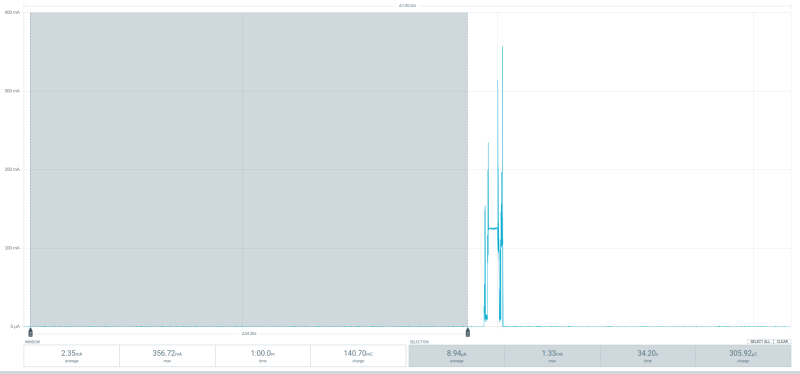
The first prototype is powered by a Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32S3 microcontoller. It is chosen because of its low deepsleep current and its built-in lipo-charging controller. To keep track of time, a ds3231 real time clock is used. It is programmed to send an alarm to the microcontroller every full hour. Once the alarm is received, the ESP wakes up from its deepsleep state and tries to connect to a wifi network. It then synchronizes the time of the rtc with an ntp server, reads the hx711 adc and sends the measurement to an mqtt broker. From there the data goes to a node red server and is then saved in an influx database. After sending, the microcontroller goes back to its deepsleep state, until its interrupted by the rtc again.
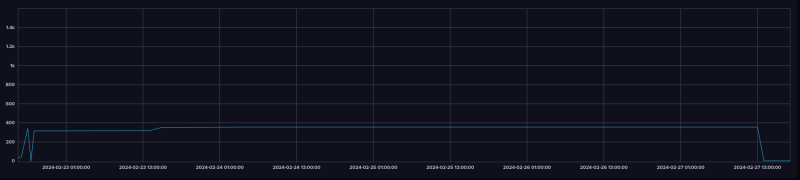
In our laboratory with a relative stable temperature the reading fluctuated by around 2 grams.
Hardware Setup
The electronics are mounted on a small piece of perfboard. The interrupt signal from the rtc needs to be pulled up while inactive. On the breakout that we used, the interrupt line is pulled to the main supply voltage of the board. In deepsleep we turn the supply voltage off to save power, so we have to cut a small trace to disconnect the resistor and use the internal pullup of the microcontroller.
 Since the normal gpios of the esp32 lose their state in deepsleep, it is important to use one that is connected to internal rtc for the interrupt.
The load cell has to be calibrated with a known weight.
Since the normal gpios of the esp32 lose their state in deepsleep, it is important to use one that is connected to internal rtc for the interrupt.
The load cell has to be calibrated with a known weight.
Power Consumption
Code
Next Steps
- bigger and water-resistant plates for the scale
- small pcb (with battery monitoring) and water resistant case for the electronics
- clean up code